brokers:
employee-onboarding-broker: # The name that the agent (broker) will be referenced by. This value is used as the asset ID in Anypoint Exchange.
card:
protocolVersion: 0.3.0 # A2A protocol version that the broker supports.
name: Employee Onboarding Broker
description: This agent acts as a broker for employee onboarding. It orchestrates the onboarding process by leveraging available tools to ensure new employees have access to all of the required systems for their daily work.
url: ${agentregistry.url}/employee-onboarding-broker # URL where the broker is hosted. Represents the preferred endpoint as declared by the broker.
provider:
organization: MuleSoft
url: https://www.mulesoft.com/
defaultInputModes: # Supported media types for input
- application/json
- text/plain
defaultOutputModes: # Supported media types for output
- application/json
skills:
- id: onboarding-agent
name: Onboarding Agent
description: This agent acts as a broker. It orchestrates the use of specialized tools and agents, including MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers, to manage employee onboarding.
examples: # Usage examples
- Onboard a new sales employee. Employee name is 'Alex Smith', email is 'alex.smith@example.com', and phone number is '555-123-4567'.
inputModes:
- application/json
- text/plain
outputModes:
- application/json
- text/plain
tags: [onboarding] # Categorization tags
capabilities:
streaming: false
pushNotifications: false
stateTransitionHistory: false
extensions:
- uri: "https://example.com/ext/konami-code/v1"
description: "Description text"
required: false
params:
hints: "Hint text"
version: 1.0.0 # Agent (broker) versionAgent Network Project File Reference
Configure and publish your agent network using two key files: agent-network.yaml and exchange.json.
The agent-network.yaml file defines agent behaviors, tools, and inter-agent communication, while exchange.json contains metadata for Anypoint Exchange publication. Understanding these files enables you to orchestrate multi-agent systems with external services and manage asset dependencies across your organization.
Agent Network YAML
The agent network YAML file defines a structured configuration for multi-agent systems, enabling orchestration of AI agents with external services, tools, and inter-agent communication. This format provides a declarative way to define agent capabilities, dependencies, and service integrations.
For example, think of the YAML as your organizational chart for digital labor. Each internal organization (for example, HR, IT, Sales, or Engineering) has a hierarchical structure through which actors collaborate. Jobs are split into tasks and assigned.
Just like with human labor, digital agents require coordination. We call these coordinators "brokers". These are special types of agents in your agent network capable of receiving a user prompt, identifying the goal, determining the necessary steps to be carried out, and delegating each step to the proper agent, even if the agent is part of a different broker.
The agent-network.yaml file uses these sections.
Brokers Section
brokers
This section defines the AI assets in your agent network. A broker is an intelligent routing service that coordinates task delegation across specialized agents in your enterprise. It’s defined by the agents and MCP servers it can use to accomplish tasks. The broker name is used as the assetId in the exchange.json file. The groupId defaults to the associated business group value used in exchange.json.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|---|
|
The list of brokers defined in your agent network. |
Object |
Object with property names matching this pattern: |
The broker element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Agent card definition. |
Object |
Refer to the |
Yes |
|
Broker specification. |
Object |
Refer to the |
Yes |
Card Section
card
This section adheres to the Agent-to-Agent (A2A) specification v0.3.0 and describes the broker’s contract, skills, and capabilities. This is a standard A2A agent card as defined in the Agent2Agent (A2A) Protocol specification..
The card element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The version of the A2A protocol this agent supports. |
String |
A2A protocol version (for example, "0.3.0") |
No |
|
A human-readable name for the agent. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
A human-readable description of the agent, assisting users and other agents in understanding its purpose. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
The preferred endpoint URL for interacting with the agent. This URL must support the transport specified by 'preferredTransport'. |
String (URI) |
Valid URI string |
No |
|
The transport protocol for the preferred endpoint (the main 'url' field). |
String |
|
No |
|
A list of additional supported interfaces (transport and URL combinations). |
Array |
Array of interface objects (See AdditionalInterfaces properties) |
No |
|
An optional URL to an icon for the agent. |
String (URI) |
Valid URI string |
No |
|
Information about the agent’s service provider. |
Object |
Object with provider properties (See provider properties) |
No |
|
The agent’s own version number. The format is defined by the provider. |
String |
Version string (for example, "1.0.0") |
No |
|
An optional URL to the agent’s documentation. |
String (URI) |
Valid URI string |
No |
|
A declaration of optional capabilities supported by the agent. |
Object |
Object with capability properties (See capabilities properties) |
No |
|
A declaration of the security schemes available to authorize requests. |
Object |
Keys are scheme names; values follow the OpenAPI 3.0 Security Scheme Object |
No |
|
A list of security requirement objects that apply to all agent interactions. |
Array |
Array of security requirement objects |
No |
|
Default set of supported input MIME types for all skills, which can be overridden on a per-skill basis. |
Array of strings |
Array of MIME type strings (for example, |
No |
|
Default set of supported output MIME types for all skills, which can be overridden on a per-skill basis. |
Array of strings |
Array of MIME type strings (for example, |
No |
|
The set of skills, or distinct capabilities, that the agent can perform. |
Array |
Array of skill objects (See skills properties) |
No |
|
Indicates if the agent can provide an extended agent card with additional details to authenticated users. |
Boolean |
|
No |
|
JSON Web Signatures computed for this AgentCard. |
Array |
Array of signature objects |
No |
provider Properties
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The name of the organization providing the agent. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
The URL of the organization. |
String (URI) |
Valid URI string |
No |
additionalInterfaces Properties
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The URL for this additional interface. |
String (URI) |
Valid URI string |
Yes |
|
The transport protocol for this interface. |
String |
|
Yes |
skills Properties
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Unique identifier for the skill. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
A human-readable name for the skill. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
A description of what this skill does. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
Usage examples demonstrating how to use this skill. |
Array of strings |
Array of example strings |
No |
|
Supported input MIME types for this skill (overrides defaultInputModes). |
Array of strings |
Array of MIME type strings |
No |
|
Supported output MIME types for this skill (overrides defaultOutputModes). |
Array of strings |
Array of MIME type strings |
No |
|
Categorization tags for this skill. |
Array of strings |
Array of tag strings |
No |
capabilities Properties
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Indicates if the agent supports streaming responses. |
Boolean |
|
No |
|
Indicates if the agent supports push notifications. |
Boolean |
|
No |
|
Indicates if the agent maintains state transition history. |
Boolean |
|
No |
|
List of extension capabilities supported by the agent. |
Array |
Array of extension objects (See extensions properties) |
No |
extensions
Example
The extensions element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
URI identifying the extension. |
String (URI) |
Valid URI string |
No |
|
Description of the extension. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
Indicates if this extension is required. |
Boolean |
|
No |
|
Parameters for the extension. |
Object |
Any object (for example, |
No |
Spec Section
spec
This section configures the broker’s internal implementation. You can think of this section as the source code for your broker.
In this section, specify the LLM to use, custom instructions, available tools, and error handling. The links section defines the agents that are available to this broker. Essentially, the links section is where you define the agent network.
The spec element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
LLM configuration for the broker. |
Object |
See LLM |
Yes |
- |
|
Set of custom instructions that will inform the orchestration. |
Array of strings |
Array of instruction strings |
Yes |
- |
|
Defines the list of agents that this agent connects to. |
Array |
Array of link objects (See Links) |
Yes |
- |
|
The maximum number of steps that a task can take. Useful for keeping orchestrations from running too long and consuming too many tokens. |
Integer |
Positive integer |
No |
25 |
|
The maximum number of errors that the orchestrator will attempt to recover from before returning a failed status. |
Integer |
Positive integer |
No |
3 |
|
A timeout (in seconds) for how long each orchestration task should run. |
Integer |
Positive integer |
No |
60 |
|
The tools available to this broker. |
Array |
Array of tool objects (See Tools) |
No |
- |
|
Policy bindings to be applied. |
Array |
Array of PolicyBinding objects (See Policies) |
No |
- |
LLM Section
llm
The value of this section is a reference to one of the LLMs defined in Anypoint Exchange or in the llmProviders section of agent-network.yaml. Because it’s a reference, you can choose to share the same LLM across all the brokers in your agent network. Or, you can have different brokers use different LLMs to better suit their tasks.
For more information about supported LLMs, see Large Language Models.
The llm element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The reference to the LLM to be used by the orchestrator. |
String |
See LLM Providers |
Yes |
|
Connection reference. |
String |
See Connections |
No |
|
The name of the model to use. |
String |
Model name string |
Yes |
|
OpenAI specific configuration settings. |
Object |
Object with OpenAI settings |
No |
|
Constrains reasoning effort for reasoning models. Useful for managing performance and reason-token usage. |
String |
|
No |
|
Controls randomness in the output. Requires GPT-5.1 and |
Number |
Any number |
No |
|
Nucleus sampling parameter. Requires GPT-5.1 and |
Number |
Any number |
No |
|
Number of most likely tokens to return at each position. Requires GPT-5.1 and |
Integer |
Any integer |
No |
|
Maximum number of tokens to generate. |
Integer |
Any integer |
No |
|
Gemini-specific configuration settings. |
Object |
Object with Gemini settings |
No |
|
Sets a token budget for the reasoning phase. (Applies only to Gemini 2.5 series.) |
Integer |
|
No |
|
Controls the depth of the reasoning process. (Applies only to Gemini 3 series.) |
String |
|
No |
|
Controls randomness. |
Number |
For Gemini 3 and Gemini 2.5, Google recommends keeping this at |
No |
|
Nucleus sampling parameter. |
Number |
Any number |
No |
|
Whether to return log probabilities. |
Boolean |
true or false |
No |
|
Maximum number of tokens that can be generated in the response. |
Integer |
Any integer |
No |
Instructions Section
instructions
Provides instructions that are specific to the broker. Instructions often focus on business-oriented concerns. For example, here’s instructions for an employee onboarding broker.
instructions:
- |
You're an Employee Onboarding Broker. Coordinate onboarding of a new employee across the systems needed for day-to-day work.
## The process for onboarding an employee is:
- Onboard in HR: Create the new employee record. Fetch the address using available tools. Don't ask for the address unless you're not sure how to get it.
- Onboard in CRM: Create the employee's CRM profile.
- Send a Slack status update using SlackMcpServer.send_status_update (include contextId from input).
- Request an employee laptop in Zendesk and initiate the employee badge request.
- Send another Slack status update using SlackMcpServer.send_status_update (include contextId from input).
- IT system setup: Provision the ping ID system for the employee.
## Final Response
- Return a plain-text human-readable summary of all steps and actions taken, formatted as a bulleted list. Don't include tool names in the summary.Here’s another example of instructions for a customer service broker. This broker coordinates management of customer-reported incidents.
instructions:
- |
You're an Incident Management Broker. Your primary responsibility is to coordinate the resolution of incidents reported by customers.
The process for incident management is:
1. Fetch CRM case details: Retrieve the latest critical case details for the customer.
2. Fetch entitlement details: Obtain the customer's entitlement information.
3. Fetch on-call engineer: Identify the current on-call engineer for the incident.
4. Create Slack war room and invite on-call engineer: Set up a Slack war room channel and invite the on-call engineer.
5. Summarize actions: Provide a clear, human-readable summary of the steps performed, including information about the created Slack channel and the on-call engineer assigned.You don’t have to provide instructions like "split the prompt into tasks", or "select the best tool". The broker does that on its own.
The instructions element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Set of custom instructions that will inform the behavior of the broker. |
Array of strings |
Array of instruction strings. Each item in the array is a string containing custom instructions for the broker |
Yes |
|
Individual instruction string. |
String |
Any string value. Typically contains business-oriented instructions, process descriptions, or guidelines for the broker’s behavior. |
- |
Tools Section
tools
Tools provide agents with external capabilities. When a broker needs to access an external service that’s not another agent, it reaches out to an MCP server.
By default, the broker has access to all the tools available on the MCP server. However, most modern LLMs can only handle around 20 to 25 tools per context before starting to hallucinate. Limit the available tools to the minimum needed. You can apply that filtering through the allowed list.
Example
tools:
- mcp:
ref:
name: talent-pool-mcp # Exchange asset ID of MCP server. By default, the groupId for this asset is the same as that in exchange.json.
allowed: # Allowlist specific tools
- TalentPoolMcpServer.match_email_to_address
headersToPropagate: [Authorization, X-Request-Id] # Optional. Header names to forward when invoking this tool.
- mcp:
ref:
name: slack-mcp
allowed:
- SlackMcpServer.send_status_updateThe tools element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The reference to the MCP server that is available to this broker. |
String |
See MCP Servers |
Yes |
|
Connection reference. |
String |
See Connections |
No |
|
Filters the list of tools advertised by the MCP server to only those in this list. Mutually exclusive with 'denied'. |
Array of strings |
Array of tool name strings |
No |
|
The names of the request headers to propagate when the broker invokes this tool. |
Array of strings |
Array of header name strings |
No |
Links Section
links
This section is the most important part of the spec, as it defines the agents that are available to a broker. It enables interagent communication and orchestration. The broker relies on the agents linked here to execute the appropriate actions to complete a user’s goal.
Example 1
links:
- agent:
ref:
name: hr-agent # Exchange asset ID of the linked agent. By default, the groupId for this asset is the same as that in exchange.json.
namespace: # Optional. If the asset was defined in a different business group, set the corresponding groupId here.
headersToPropagate: [Authorization, X-Correlation-Id] # Optional. Header names to forward when invoking this agent.
- agent:
ref:
name: badging-agent
- agent:
ref:
name: crm-agent
- agent:
ref:
name: zendesk-agent
- agent:
ref:
name: it-agentKeep this section short. Don’t add all available agents. Just like tools, excess values here lead to drops in agent network accuracy and determinism.
Instead, use a multi-level hierarchical approach. This favors traceability and management and helps keep context sizes in check.
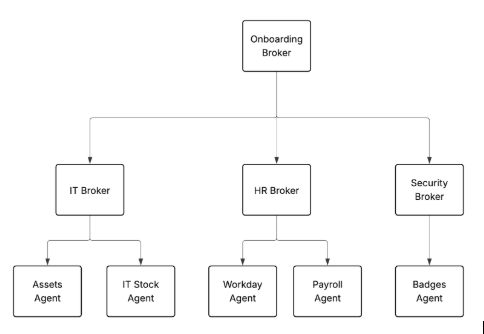
Example 2
In this example, the Onboarding Broker orchestrates the process of onboarding a new hire. It orchestrates work with the IT, HR and security brokers, which also happen to be brokers in the same agent network.
Assets, IT Stock, HR, Payroll, and Badges agents are also called leaf agents. These aren’t brokers but preexisting agents whose purpose isn’t to coordinate work, but to act.
The links element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Defines the list of agents that this agent connects to. This defines the agent network and enables inter-agent communication and orchestration. |
Array |
Array of link objects |
Yes |
|
A link object in the links array. |
Object |
Object with |
Yes |
|
Agent connection configuration. |
Object |
Object with agent properties |
Yes |
|
Exchange asset ID of the linked agent. This references the |
String |
Asset ID string (for example, "hr-agent", "crm-agent"). By default, the groupId for this asset is the same as that in exchange.json |
Yes |
|
Business group ID (groupId) where the asset is defined. Use this when the asset was defined in a different business group than the current one. |
String |
Group ID string. To find the groupId, look in the |
No |
|
Connection reference. |
String |
See Connections. This references a connection defined in the |
No |
|
The names of the request headers to propagate when the broker invokes this agent. |
Array of strings |
Array of header name strings |
No |
Policies Section
policies
The policies section contains the list of policies to apply to the broker. It contains a reference to the policy that needs to be added as a dependency to the agent network project.
Example
policies:
- ref:
name: # Exchange asset ID of the policy. By default, the groupId for this asset is the same as that in exchange.json.
namespace: # Optional. If the policy was defined in a different business group, set the corresponding groupId here.
configuration:
policyConfig1: policyConfig1ValueApply policies at the broker or at the connection. Reference the policy definition and apply the configuration.
For more information about applying policies via Flex Gateway in Local Mode, see:
|
When you add governance policies to your project, those policies persist between deployments. However, if you add governance policies at runtime, those policies won’t persist. |
The policies element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Policy reference. |
String |
See Policies |
Yes |
|
Policy configuration. |
Object |
Any object |
Yes |
Error Handling
Use these properties to handle error scenarios. Define these properties within the spec section of a broker configuration.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The maximum number of steps that a task can take. Useful for keeping orchestrations from running too long and consuming too many tokens. |
Integer |
Positive integer |
No |
25 |
|
The maximum number of errors that the orchestrator will attempt to recover from before returning a failed status. |
Integer |
Positive integer |
No |
3 |
|
A timeout (in seconds) for how long each orchestration task should run. |
Integer |
Positive integer (seconds) |
No |
60 |
Error Handling Considerations
-
maxNumberOfLoops-
Each step in an orchestration consumes tokens.
-
Complex tasks may require more steps.
-
Simple tasks should complete with fewer steps.
-
The default of 25 maximum loops is suitable for most use cases.
-
-
maxConsecutiveErrors-
Allows the orchestrator to retry failed operations.
-
Prevents infinite retry loops.
-
Default of
3attempts provides a balance between resilience and failure detection. After reaching this limit, the orchestration returns a failed status.
-
-
taskTimeoutSecs-
Applies to each individual orchestration task.
-
Accounts for network latency and external service response times.
-
Default of 60 seconds is suitable for most API-based operations. Tasks exceeding this timeout are terminated.
-
Agents Section
agents
Reference agents defined in a different agent network, or another agent used in your company. Any agent is valid, as long as it supports A2A as its communication protocol. For more information, see af-agent-networks.adoc#a2a-protocol
Example
agents:
hr-agent: # Used as the assetId of the asset published to Anypoint Exchange. The default groupId is the associated value used in exchange.json.
metadata:
platform: azure
protocol: a2a
badging-agent:
metadata:
platform: azure
protocol: a2a
crm-agent:
metadata:
platform: azure
protocol: a2a
zendesk-agent:
metadata:
platform: azure
protocol: a2a
it-agent:
metadata:
platform: azure
protocol: a2aThe agents element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A label for this agent. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
A description for this agent. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
Tags associated with this agent. |
Array |
Array of string values |
No |
|
Agent card definition. |
Object |
See Card |
No |
|
Agent metadata configuration. |
Object |
Object with |
Yes |
|
The name of the platform running this agent. For example, Bedrock, AgentForce, etc. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
The name of the protocol. For example, a2a. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
Defines the list of agents that this agent connects to. |
Array |
Array of objects with |
No |
|
Defines the list of tools that this agent connects to. |
Array |
Array of objects with |
No |
MCP Servers Section
mcpServers
This section lists the MCP servers in your agent network. Use these servers to obtain relevant context and generate notifications. To apply governance to an MCP server using the agent network file, it must be in your agent-network.yml file or published to Anypoint Exchange as an asset.
Example
mcpServers:
talent-pool-mcp: # Value used as the assetId in exchange.json. The groupId defaults to the associated value used in exchange.json.
metadata:
transport: # Communication method
kind: streamableHttp # HTTP-based transport
path: /mcp
# OR
sse: # Server-Sent Events transport
ssePath: /sse
messagesPath: /messages
tools: # Server-level tool filtering
allowed: [tool1, tool2]
slack-mcp:
metadata:
transport:
kind: streamableHttp
path: /mcpWe support both MCP streamableHttp and SSE transports, but we recommend streamableHttp.
Just like in the brokers section, an allowed attribute is available to filter the available tools. The allowed attribute in the brokers section is more granular and applied only to that specific broker. In the mcpServers section, this attribute applies to the MCP server as a whole, filtering at the group level.
The mcpServers element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A label for this MCP server. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
A description for this MCP server. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
Tags associated with this MCP server. |
Array |
Array of string values |
No |
|
MCP server metadata configuration. |
Object |
See MCP Servers |
Yes |
|
Communication method configuration for the MCP server. |
Object |
Object with transport properties |
No |
|
The transport protocol type. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
The path for the |
String |
Any string value (for example, |
No |
|
The SSE path for Server-Sent Events transport. |
String |
Any string value (for example, |
No |
|
The messages path for Server-Sent Events transport. |
String |
Any string value (for example, |
No |
|
Server-level tool filtering configuration. |
Object |
Object with |
No |
|
Filters the list of tools advertised by the MCP server to only those in this list. |
Array |
Array of tool name strings |
No |
LLMProviders Section
llmProviders
Configure the LLMs the brokers use for reasoning. For more information about supported LLMs, see Large Language Models.
The llmProviders element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The list of LLM providers defined as part of this network. |
Object |
Object with property names matching pattern: |
- |
|
A label for this LLM. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
The description of this LLM. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
LLM metadata configuration. |
Object |
Either WellKnownLLM or CustomLLM object (See metadata properties) |
Yes |
metadata Properties
The metadata property uses a oneOf structure, so it must be either a WellKnownLLM or a CustomLLM object but not both.
The WellKnownLLM object has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The LLM platform provider. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
List of available models for this platform. |
Array of strings |
Array of model name strings |
No |
The CustomLLM object has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The LLM platform provider name. |
String |
Any string value |
Yes |
|
List of available models for this platform. |
Array of strings |
Array of model name strings |
No |
|
Reference to the transcoder policy. |
String |
See Policies |
No |
Connections Section
connections
The connections section defines one or more connections to instances of an agent network asset. For example, if an agent is deployed multiple times across regions and environments, you can define a connection for each deployed agent instance, regardless of whether it’s used by a broker or not.
Connections are elements that are deployed, but they don’t have Exchange assets that represent them. They’re connected to assets (agents, MCP servers, LLMs). They’re deployed in API Manager in the egress gateway.
To define multiple connections for the same asset, put them in a resource file and reference the file in this section.
Example
connections:
hr-agent:
kind: agent
ref:
name: hr-agent # Use the same name as in the associated entry in the agents section or use the Exchange asset ID.
spec:
url: https://hr-a2a-agent-inkbh1.paga8m.usa-w1.cloudhub.io/hr-agent/
authentication:
kind: oauth2-client-credentials
token:
bodyEncoding: form
timeout: 300
url: test.com # Use a variable
clientId: clientId # Use a variable like ${hrAgent.clientId} and define in in exchange.json so the user is prompted for the value at deployment.
clientSecret: clientSecret # Use a variable
badging-agent:
kind: agent
ref:
name: badging-agent
spec:
url: https://badge-agent-inkbh1.paga8m.usa-w1.cloudhub.io/badge-agent/
authentication:
kind: oauth2-client-credentials
token:
bodyEncoding: form
timeout: 300
url: test.com
clientId: clientId
clientSecret: clientSecret
crm-agent:
kind: agent
ref:
name: crm-agent
spec:
url: https://crm-a2a-agent-inkbh1.paga8m.usa-w1.cloudhub.io/crm-agent/
authentication:
kind: oauth2-client-credentials
token:
bodyEncoding: form
timeout: 300
url: test.com
clientId: clientId
clientSecret: clientSecret
zendesk-agent:
kind: agent
ref:
name: zendesk-agent
spec:
url: https://zendesk-a2a-agent-inkbh1.paga8m.usa-w1.cloudhub.io/zendesk/
authentication:
kind: oauth2-client-credentials
token:
bodyEncoding: form
timeout: 300
url: test.com
clientId: clientId
clientSecret: clientSecret
it-agent:
kind: agent
ref:
name: it-agent
spec:
url: https://ping-id-a2a-agent-inkbh1.paga8m.usa-w1.cloudhub.io/pingid/
authentication:
kind: oauth2-client-credentials
token:
bodyEncoding: form
timeout: 300
url: test.com
clientId: clientId
clientSecret: clientSecret
my-openAI:
kind: llm
ref:
name: my-openAI
spec:
url: https://api.openai.com/v1/
configuration:
apiKey: ${openai.apiKey}
talent-pool-mcp:
kind: mcp
ref:
name: talent-pool-mcp
spec:
url: https://talent-pool-mcp-server-inkbh1.paga8m.usa-w1.cloudhub.io/
authentication:
kind: apiKey
apiKey: ${talentPool.apiKey} # Define variable in exchange.json
headerName: X-MCP-API-Key # Optional, defaults to Authorization
slack-mcp:
kind: mcp
ref:
name: slack-mcp
spec:
url: https://slack-mcp-server-inkbh1.paga8m.usa-w1.cloudhub.io/
authentication:
kind: apiKey
apiKey: ${slack.apiKey} # Define variable in exchange.json
headerName: X-API-KeyThe connections element has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The list of connections defined as part of this network. |
Object |
Object with property names matching pattern: |
- |
|
The type of connection. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
Reference to the asset this connection is for. |
Object |
Object with reference properties (See ref properties) |
Yes |
|
Exchange asset ID of the connected asset. |
String |
Asset ID string. For agents, use the same name as in the associated entry in the agents section or use the Exchange asset ID. For LLMs, use the name from llmProviders. For MCP servers, use the name from mcpServers |
Yes |
|
Business group ID (groupId) where the asset is defined. Use this when the asset was defined in a different business group than the current one. |
String |
Group ID string. To find the groupId, look in the |
No |
|
Connection specification. Properties vary by connection kind. |
Object |
Object with spec properties (See Spec) |
Yes |
|
The URL for the connection endpoint. |
String |
Valid URL string |
Yes (for agent and llm), No (for mcp) |
|
Authentication configuration for the connection. |
Object |
Authentication object (See Authentication types) |
No |
|
The type of authentication. |
String |
|
Yes (when authentication is specified) |
|
The username for basic authentication. |
String |
Any string value |
Yes (for basic auth) |
|
The password for basic authentication. |
String |
Any string value |
Yes (for basic auth) |
|
The name of the header in which to set the key. If not specified, 'Authorization' is set by default. |
String |
Any string value |
No |
|
The client ID for OAuth 2.0 or API key client credentials authentication. |
String or Object |
|
Yes (for oauth2-client-credentials and apikey-client-credentials) |
|
The client secret for OAuth 2.0 or API key client credentials authentication. |
String or Object |
|
Yes (for oauth2-client-credentials and apikey-client-credentials) |
|
Configuration on how to fetch the OAuth 2.0 token. |
Object |
Object with token properties |
Yes (for oauth2-client-credentials) |
|
The URL of the token provider. |
String |
Valid URL string |
Yes |
|
Time in seconds to wait for the service to return the token. |
Number |
Any number |
No |
|
The encoding format for the token request body. |
String |
|
No |
|
An array of scopes to request for OAuth 2.0. |
Array |
Array of scope strings |
No |
|
The value of the API key for API key authentication. |
String |
Any string value |
Yes (for apiKey) |
|
LLM-specific configuration object. |
Object |
Any object |
Yes (for llm connections) |
|
Policy bindings to be applied to the connection. |
Array |
Array of PolicyBinding objects (See Policies) |
No |
|
Policy reference. |
Object |
Object with |
Yes |
|
Exchange asset ID of the policy. By default, the groupId for this asset is the same as that in exchange.json. |
String |
Asset ID string |
Yes |
|
Optional. If the policy was defined in a different business group, set the corresponding groupId here. |
String |
Group ID string |
No |
|
Policy configuration. |
Object |
Any object |
Yes |
Connection Resolution
Connection resolution happens at deployment time. The connection reference can be explicit or implicit.
Explicit
In this example, the connection to use is weather-agent-connection. At deployment, it validates that a connection with the given name exists in the egress gateway on the specified environment.
Example
- agent:
ref:
name: weather-agent
connection:
ref:
name: weather-agent-connectionImplicit
If a connection isn’t specified, it defaults to a connection whose name matches the target asset’s name.
In this example, at deployment a connection to the specified agent asset (weather-agent) is searched for. If it exists, it’s injected. If not, it fails with an exception.
Example
- agent:
ref:
name: weather-agentAuthentication Types
Connection authentication is always expressed in accordance with Open API authentication methods.
These examples show how to define each supported authentication type in YAML.
Both agents and MCP servers support the same authentication types with custom header capabilities API Key Authentication and Basic Authentication.
Basic Authentication
authentication:
kind: basic
username: "username"
password: "password"Using custom header:
kind: basic
username: "username"
password: "password"
headerName: X-API-Authorization # Custom header instead of default "Authorization"The basic authentication has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication type. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
The username for authentication. |
String |
Any string |
Yes |
|
The password for authentication. |
String |
Any string |
Yes |
|
The name of the header in which to set the credentials. If not specified, |
String |
Any string |
No |
OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials
authentication:
kind: oauth2-client-credentials
clientId: "client_id"
clientSecret: "client_secret"
token:
url: "https://oauth.provider.com/token"
bodyEncoding: form
timeout: 300
scopes: ["read", "write"] # OptionalThe oauth2-client-credentials authentication has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication type. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
The client ID. |
String |
Any string |
Yes |
|
The client secret. |
String |
Any string |
Yes |
|
Configuration for fetching the token. |
Object |
Object with token properties |
Yes |
|
The URL of the token provider. |
String |
Valid URL |
Yes |
|
Time in seconds to wait for the service to return the token. |
Number |
Any number |
No |
|
The encoding format for the token request body. |
String |
|
No |
|
An array of scopes to request. |
Array |
Array of scope strings |
No |
Anypoint Client Credentials
authentication:
kind: apikey-client-credentials
clientId: "client_id"
clientSecret: "client_secret"The apikey-client-credentials authentication has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication type. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
The client ID. |
Object |
Object with |
Yes |
|
The client secret. |
Object |
Object with |
Yes |
API Key Authentication
authentication:
kind: api-key
apiKey: ${agent.apiKey} # Define variable in exchange.json
headerName: X-API-Key # Optional, defaults to AuthorizationUsing custom header:
authentication:
kind: apiKey
apiKey: ${agent.apiKey}
headerName: X-Custom-Auth-Token # Custom header nameThe apiKey authentication has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication type. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
The value of the API key. |
String |
Any string |
Yes |
|
The name of the header in which to set the key. If not specified, |
String |
Any string |
No |
In-Task Authorization Code
Use in-task authorization code when the connection needs secondary credentials obtained during a task using the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code flow. OAuth2 tokens are extracted from message data and injected into the Authorization header for upstream calls. This supports step-up or in-task authentication (for example, when a user must re-authenticate for a sensitive action). For more information about the associated policy, see A2A In-Task Authorization Code Policy.
authentication:
kind: in-task-authorization-code
secondaryAuthProvider: providerName
authorizationEndpoint: https://oauth.provider.com/authorize
tokenEndpoint: https://oauth.provider.com/token
scopes: Read
redirectUri: https://oauth.provider.com/callback
responseType: code
tokenAudience: https://api.example.com/agents/my-agent
codeChallengeMethod: S256
bodyEncoding: form
challengeResponseStatusCode: 200 #Optional, Status code for challenge response. Default: 200.
tokenTimeout: 300 #Optional. Timeout in seconds for token requests. Default: 300.The in-task-authorization-code authentication has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication type. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
OAuth2 authorization endpoint URL. Used to generate the authentication challenge. |
String |
Valid URL |
Yes |
|
OAuth2 token endpoint URL. Used to generate the authentication challenge. |
String |
Valid URL |
Yes |
|
OAuth2 scopes required for step-up authentication. |
String |
Space- or comma-separated scope list (for example, |
Yes |
|
OAuth2 redirect URI the client uses in the authorization flow. |
String |
Valid URI |
Yes |
|
Name of the IdP (for example, |
String |
Any string |
No |
|
OAuth2 response type. |
String |
Typically |
No |
|
PKCE code challenge method. |
String |
Typically |
No |
|
Intended recipient of the token (for example, |
String |
Any string |
No |
|
Encoding for the token request body. |
String |
|
No |
|
Timeout in seconds for token requests. |
Integer |
Positive integer. Default: 300 |
No |
|
HTTP status code returned for auth-required challenge responses. Typically 200 for JSON-RPC compatibility. |
Integer |
HTTP status code. Default: 200 |
No |
OAuth 2.0 OBO Credential Injection
This authentication type supports OAuth 2.0 Token Exchange and Microsoft Entra ID On-Behalf-Of protocols. For more information about the associated policy, see OAuth 2.0 OBO Credential Injection Policy.
Using OAuth 2.0 Token Exchange:
authentication:
kind: oauth2-obo
flow: oauth2-token-exchange
tokenEndpoint: https://oauth.provider.com/token
clientId: clientId
clientSecret: clientSecret
targetType: audience
targetValue: https://api.example.com/agents/my-agent
scope: Read #optional, OAuth 2.0 scope to request. Required for Microsoft Entra OBO (for example, api://downstream-client-id/.default). Optional for OAuth 2.0 Token Exchange (RFC 8693).
timeout: 5000 #optional, Timeout for token exchange requests in milliseconds. Default: 10000.Using Microsoft Entra ID On-Behalf-Of:
authentication:
kind: oauth2-obo
flow: microsoft-entra-obo
tokenEndpoint: https://oauth.provider.com/token
clientId: clientId
clientSecret: clientSecret
scope: api://downstream-client-id/.default
timeout: 5000 #optional, Timeout for token exchange requests in milliseconds. Default: 10000.The oauth2-obo authentication has these properties.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Valid Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication type. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
Token exchange flow type. |
String |
|
Yes |
|
OAuth2 client ID for token exchange. |
String |
Any string |
Yes |
|
OAuth2 client secret for token exchange. |
String |
Any string |
Yes |
|
OAuth2 token endpoint URL for token exchange. |
String |
Valid URL |
Yes |
|
Parameter type for specifying the target service (audience for logical name, resource for physical URI). Used for OAuth 2.0 Token Exchange. |
String |
|
No |
|
Target audience URI or resource URI for the exchanged token. Required for OAuth 2.0 Token Exchange. |
String |
Valid URI |
Required when using |
|
OAuth scope to request. Required for Microsoft Entra OBO (e.g. |
String |
Any string |
Required for |
|
Timeout for token exchange requests in milliseconds. |
Integer |
Positive integer. Default: 10000 |
No |
exchange.json File Element
All agent network projects have an exchange.json file. This file contains asset metadata available in Anypoint Exchange after publishing your agent network assets.
Example
{
"main": "agent-network.yaml",
"name": "Employee Onboarding Network",
"classifier": "agent-network",
"organizationId": "85de5a54-1f33-4ea4-a1bf-8a65bc409179",
"descriptorVersion": "1.0.0",
"tags": [],
"groupId": "85de5a54-1f33-4ea4-a1bf-8a65bc409179",
"assetId": "employee-onboarding-network",
"version": "1.0.5",
"dependencies": [
{
"groupId": "85de5a54-1f33-4ea4-a1bf-8a65bc409179",
"assetId": "hr-agent",
"version": "1.0.21",
"classifier": "agent-metadata",
"packaging": "zip"
}
],
"metadata": {
"variables": {
"openai": {
"clientId": {
"description": "OpenAI LLM Client ID",
"default": ""
},
"clientSecret": {
"description": "OpenAI LLM Client Secret",
"default": "",
"secret": true
},
"url": {
"description": "OpenAI URL",
"default": "",
"secret": false
}
}
}
}
}These key-value pairs are important for your agent network configuration.
- groupId
-
ID of the Anypoint business group that owns your agent network and all the assets derived from it.
- assetId
-
Unique identifier for the agent network project.
- dependencies
-
Existing assets that this network needs to reference.
- variables
-
Nested in the metadata section, defines all the variables whose values shouldn’t be hardcoded in the agent network YAML file. Enter these values when publishing the agent network. Each variable has a
descriptionvalue, adefaultvalue, and asecretvalue that indicates whether it’s treated as sensitive or not.
When the agent network is published, all the assets derived from it share the same groupId (business group) defined in the exchange.json file.
Ref Element
The ref element is used in different elements in the agent network YAML, and is important for your agent network configuration.
The ref element represents another asset that exists in Exchange. The type of asset referenced depends on the context (such as agent, MCP server, LLM provider). The semantic is always that of referencing an asset that exists in Exchange, or will exist when the agent network is published (meaning, it’s defined in the file). If referenced, it’s in the dependencies section of exchange.json.
This snippet represents a link to an HR agent. The name attribute doesn’t point to the agent’s human friendly or logical name (which can change); instead, it references the assetId that hr-agent has in Exchange.
links:
- agent:
ref:
name: hr-agentThe hr-agent asset can either exist already, or can be defined in this same YAML. In either case, the Exchange assetId is the key to this reference.
In some cases, the ref element needs to point to an asset that’s defined in a different business group. For this, the ref#namespace attribute can be used to reference the asset’s groupId. To find the groupId, look in the dependencies section in the exchange.json file.
links:
- agent:
ref:
name: hr-agent
namespace: <the groupId>


