Configuring XML Cryptography
Mule runtime engine (Mule) XML Cryptography enables you to encrypt entire XML messages or just specific parts of them. Unlike PGP, which combines compression, XML encryption focuses on securing the content within XML structures. While JCE Cryptography offers broader encryption for various data, XML Cryptography is designed for the structured nature of XML, letting you precisely encrypt specific elements or the whole document. This is useful for protecting sensitive data like social security numbers or credit card details within an XML message.
Use the Cryptography Module XML operations for encryption and decryption.
| If you’re upgrading to Cryptography Module 2.1, configure the required Java dependencies so your project compiles. For details, refer to Upgrading and Migrating Cryptography Module 2.x. |
Configure XML Encryption Operations in Anypoint Studio
Follow these steps:
-
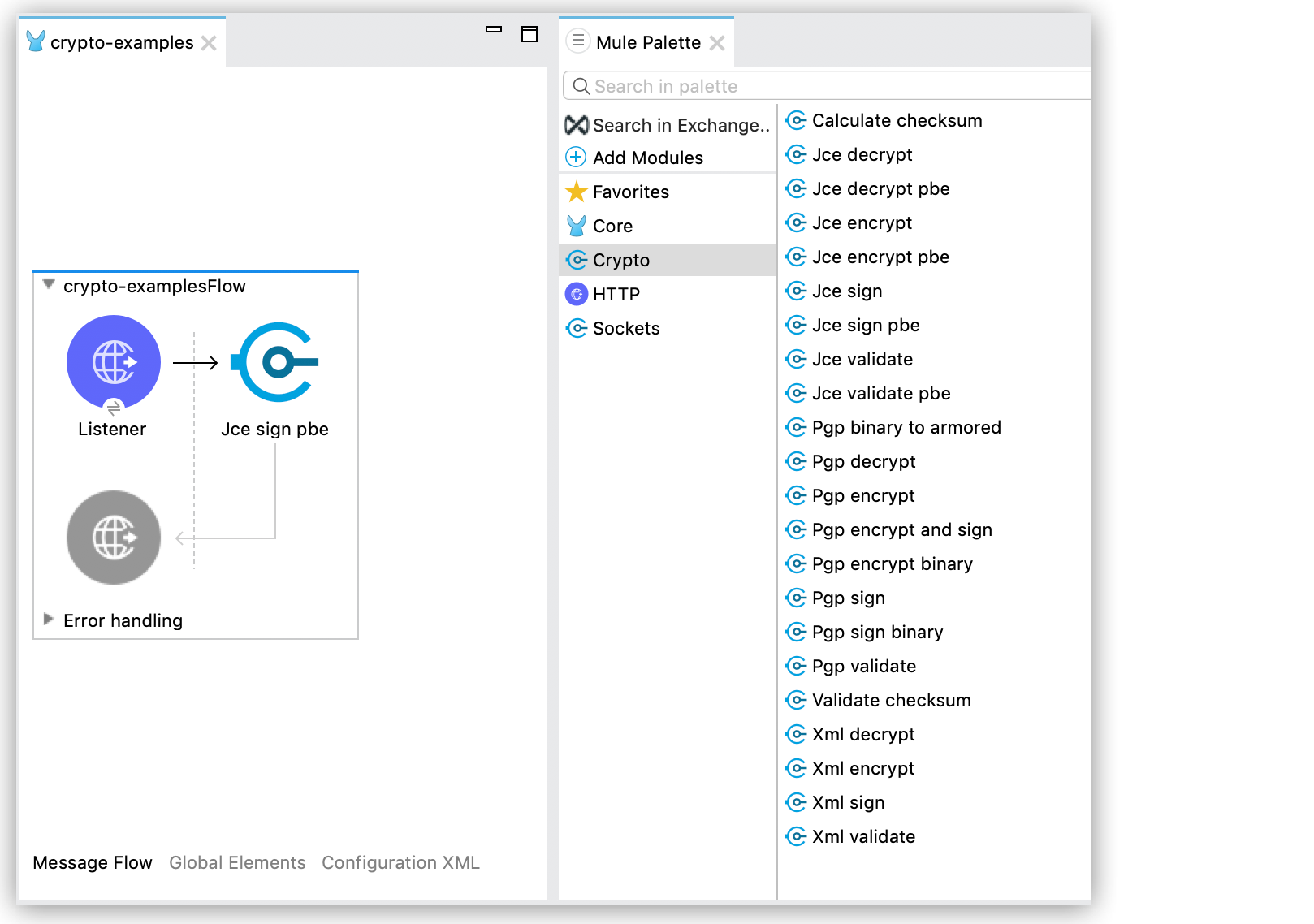
In Anypoint Studio, drag a Cryptography Module XML operation to the canvas flow.

-
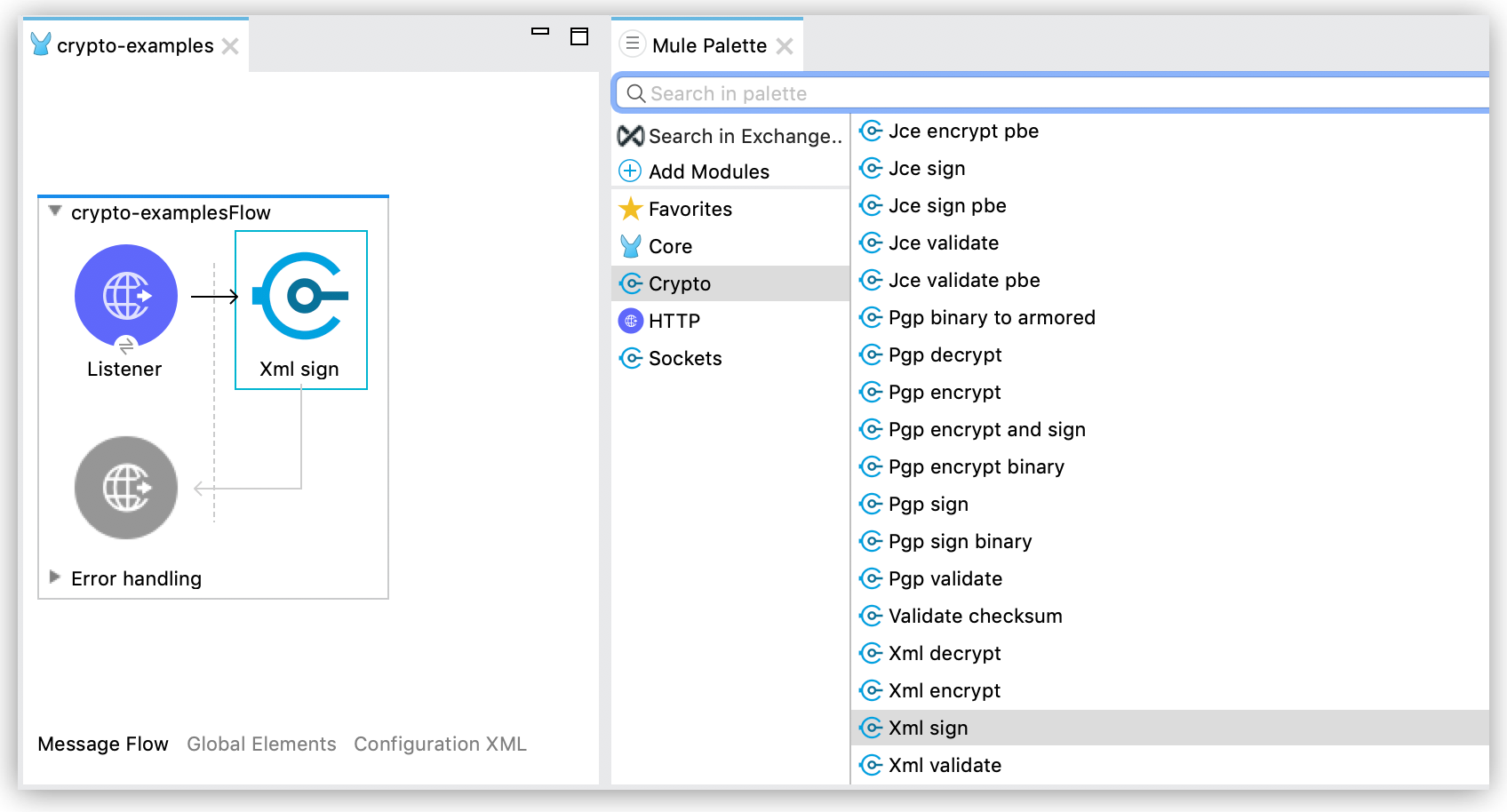
In the operation configuration window, select an existing Module configuration, or create a new one by configuring the Keystore, Type (JKS, JCEKS, PKCS12) and Password.
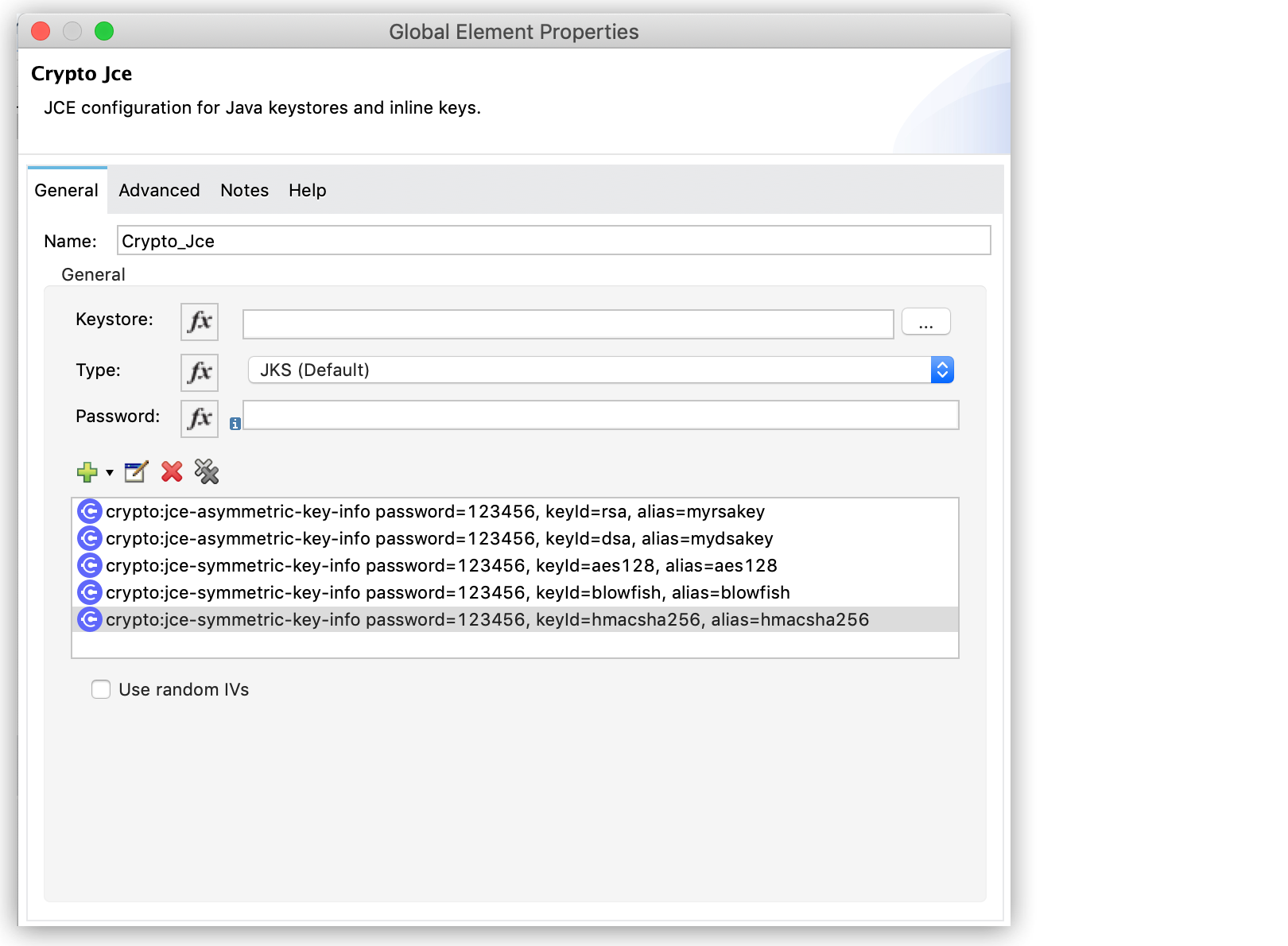
You can also add symmetric or asymmetric key information to be used in the sign operations:
-
Configure Key selection by using a Key id value previously defined in the module configuration, or define a new one for this operation:
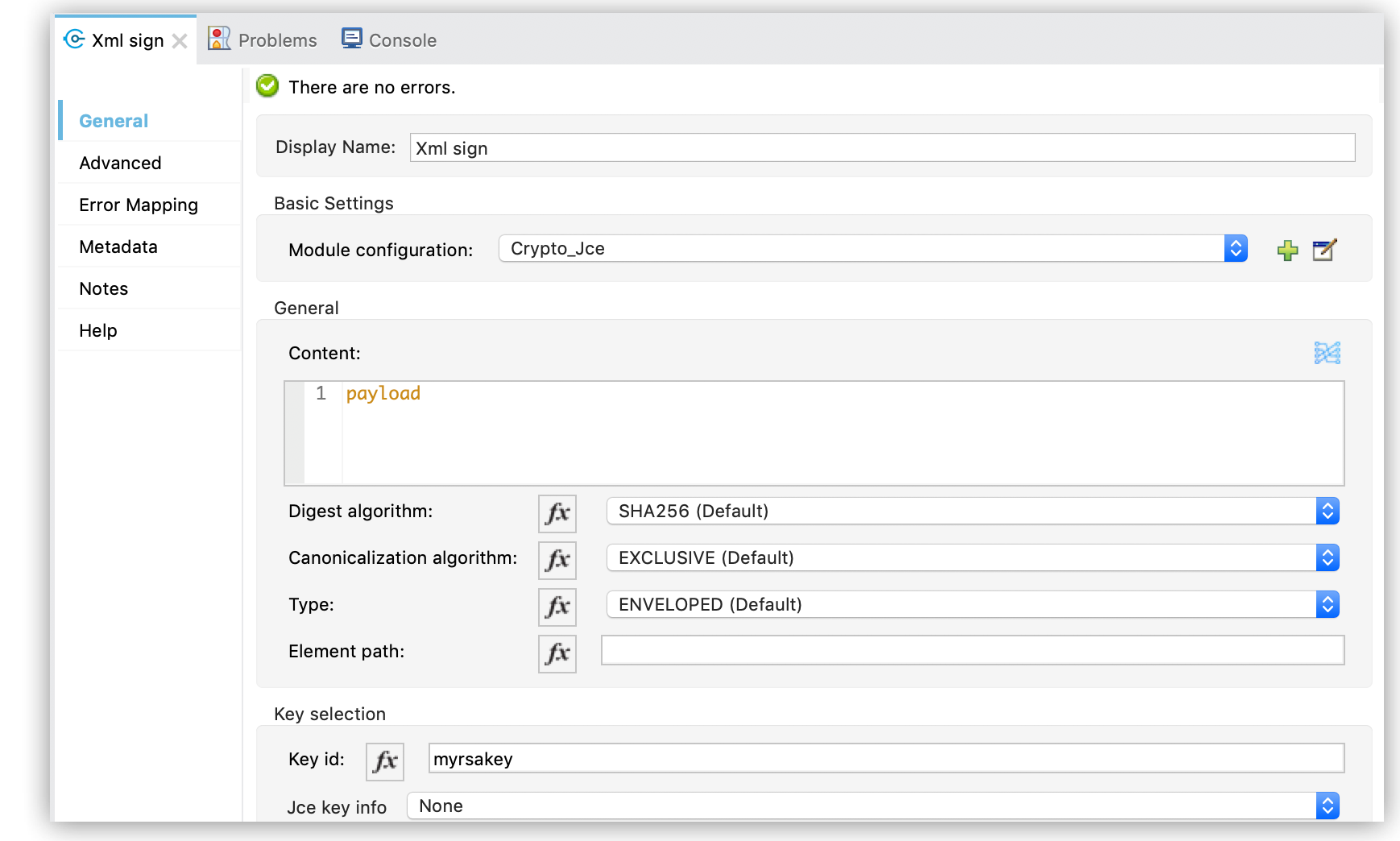
-
Select Digest Algorithm, Canonicalization Algorithm, Type, and Element path.
Encrypt
This example configures a keystore that contains a symmetric key that will be used for encryption:
<crypto:jce-config name="symmetricConfig" keystore="secret.jks" password="mule1234" type="JCEKS">
<crypto:jce-key-infos>
<crypto:jce-symmetric-key-info keyId="mySymKey" alias="aes128test" password="mule1234"/>
</crypto:jce-key-infos>
</crypto:jce-config>In this example, the Xml encrypt operation encrypts a specific element of the XML document:
<crypto:xml-encrypt config-ref="symmetricConfig" keyId="mySymKey" algorithm="AES_CBC" elementPath="//song"/>The elementPath is an XPath expression that identifies the element to encrypt. Depending on your needs, you can use a symmetric or asymmetric key for encrypting an XML document.
Decrypt
This example configures the decryption:
<crypto:jce-config name="jceConfig" keystore="keystore.jks" password="mule1234">
<crypto:jce-key-infos>
<crypto:jce-symmetric-key-info keyId="mySymKey" alias="aes128test" password="mule1234"/>
<crypto:jce-asymmetric-key-info keyId="myAsymKey" alias="test1" password="test1234"/>
</crypto:jce-key-infos>
</crypto:jce-config>In this example, the Xml decrypt operation decrypts an XML document. The operation uses the asymmetric key stored in the referenced keystore.
<crypto:xml-decrypt config-ref="jceConfig" keyId="myAsymKey"/>Depending on your needs, you can use a symmetric or asymmetric key for decryption.
Sign
This examples shows the JCE configuration to sign:
<crypto:jce-config name="asymmetricConfig" keystore="keystore.jks" password="mule1234">
<crypto:jce-key-infos>
<crypto:jce-asymmetric-key-info keyId="myAsymKey" alias="test1" password="test1234"/>
</crypto:jce-key-infos>
</crypto:jce-config>In this example, the Xml sign operation uses the asymmetric key to sign an XML document by creating an XML envelope and inserting the signature inside the content that is being signed.
<crypto:xml-sign config-ref="asymmetricConfig" keyId="myAsymKey" type="ENVELOPING" digestAlgorithm="SHA256" elementPath="/PurchaseOrder/Buyer"/>In this example, a detached XML signature is created based on an element of the XML document. Instead of being inserted in the signed content, the detached signature is returned as a separate XML element.
<crypto:xml-sign config-ref="asymmetricConfig" keyId="myAsymKey" type="DETACHED" digestAlgorithm="SHA256" elementPath="/PurchaseOrder/Buyer"/>Select the Signing Algorithm
In the Xml Sign operation, the digestAlgorithm parameter defines the hashing algorithm applied to the content before signing, for example SHA1, SHA256, or SHA512.
However, the final XML signature algorithm is not manually selected. It is automatically determined based on the type of key (RSA, DSA, EC, HMAC) configured in the module.
The signing process combines the chosen hash algorithm digestAlgorithm with the key type to produce the signature method used in the XML document.
For example:
-
An RSA key with
digestAlgorithm=SHA256results in thersa-sha256signature method. -
A DSA key with
digestAlgorithm=SHA1results in thedsa-sha1signature method. -
An EC key with
digestAlgorithm=SHA256results in theecdsa-sha256signature method.
If you want to use a different signature method, you must change the type of key in the digestAlgorithm parameter configuration. It is not currently possible to manually select the signature method within the operation.
Validate a Signature
This examples shows the JCE configuration to validate a signature:
<crypto:jce-config name="asymmetricConfig" keystore="keystore.jks" password="mule1234">
<crypto:jce-key-infos>
<crypto:jce-asymmetric-key-info keyId="myAsymKey" alias="test1" password="test1234"/>
</crypto:jce-key-infos>
</crypto:jce-config>In this example, the asymmetric key is used to validate the signature of the XML element specified by the elementPath XPath expression.
<crypto:xml-validate config-ref="asymmetricConfig" keyId="myAsymKey" elementPath="/PurchaseOrder/Buyer"/>If the document has multiple signatures, set elementPath to select the signature to validate. Specify a signed element using an XPath expression to validate the signature for that element.
Target a Custom Namespace by Using Element Path
To sign or validate an XML element that is inside a custom namespace, specify the namespace by using the XPath functions: namespace-uri and local-name.
For example, consider the following document:
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope/">
<FirstElement>
<!-- Some content -->
</FirstElement>
<SecondElement>
<!-- Additional content -->
</SecondElement>
</soap:Envelope>To target the content of FirstElement inside soap:Envelope, you specify the xmlns:soap namespace. The XML schema for xmlns:soap is defined in http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope/.
The following example shows an xml-sign operation configured to sign FirstElement:
<crypto:xml-sign
config-ref="asymmetricConfig"
keyId="myAsymKey"
type="DETACHED"
digestAlgorithm="SHA256"
elementPath="/*[namespace-uri()='http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope/' and local-name()='Envelope']/FirstElement"/>Note that the elementPath expression specifies the xmlns:soap namespace.



