Project Name
Using Anypoint Code Builder to Configure MCP Connector 1.3
To use Anypoint Code Builder to configure a connector or module, create a basic integration project in Anypoint Code Builder, add connectors and other components to your Mule application to process your business logic, and configure the attributes.
Before You Begin
Before creating an integration project, you must:
-
Set up and access the Anypoint Code Builder web or desktop IDE
-
Have credentials to access the connector’s API
-
Ensure that the Visual Studio Code Extension Pack for Java is installed.
To use this connector, you must be familiar with:
-
The connector’s API
-
Anypoint Connectors
-
Mule runtime engine (Mule)
Create a New Integration Project
To create a new integration project:
-
In the activity bar of the IDE, click the
 (Anypoint Code Builder) icon.
(Anypoint Code Builder) icon. -
From Quick Actions, click Develop an Integration:

-
Complete the following in the Develop an Integration form:
Attribute Value Unique name for your project.
This name is used as the title and name of the integration project file. For example, if the project name is "Salesforce Integration," the project file name is
salesforce-integration.Project Location
Your home directory or another directory you create. Click Browse to select a different directory for the integration project.
Don’t create the project within another project directory.
-
Select the type of project to create by selecting either the Empty Project or Template or Example card.
-
Select the Mule runtime and Java Version for your app.
-
Click Create Project.
Add the Connector to Your Integration Project
Anypoint Connectors provide operations for retrieving, modifying, and sending data to and from systems.
In addition to the built-in connectors that Anypoint Code Builder provides, you can download many other connectors from Anypoint Exchange.
To import a connector from Exchange and add it to your configuration:
-
In the Explorer view, open the configuration XML file for your project, such as
my-project-name.xml. -
Click the
 (Show Mule graphical mode) icon in the activity bar to open the canvas UI if it doesn’t open automatically.
(Show Mule graphical mode) icon in the activity bar to open the canvas UI if it doesn’t open automatically. -
Add the connector the same way you added other components from the canvas UI:
-
In the canvas UI, click the
 (Add component) icon.
(Add component) icon. -
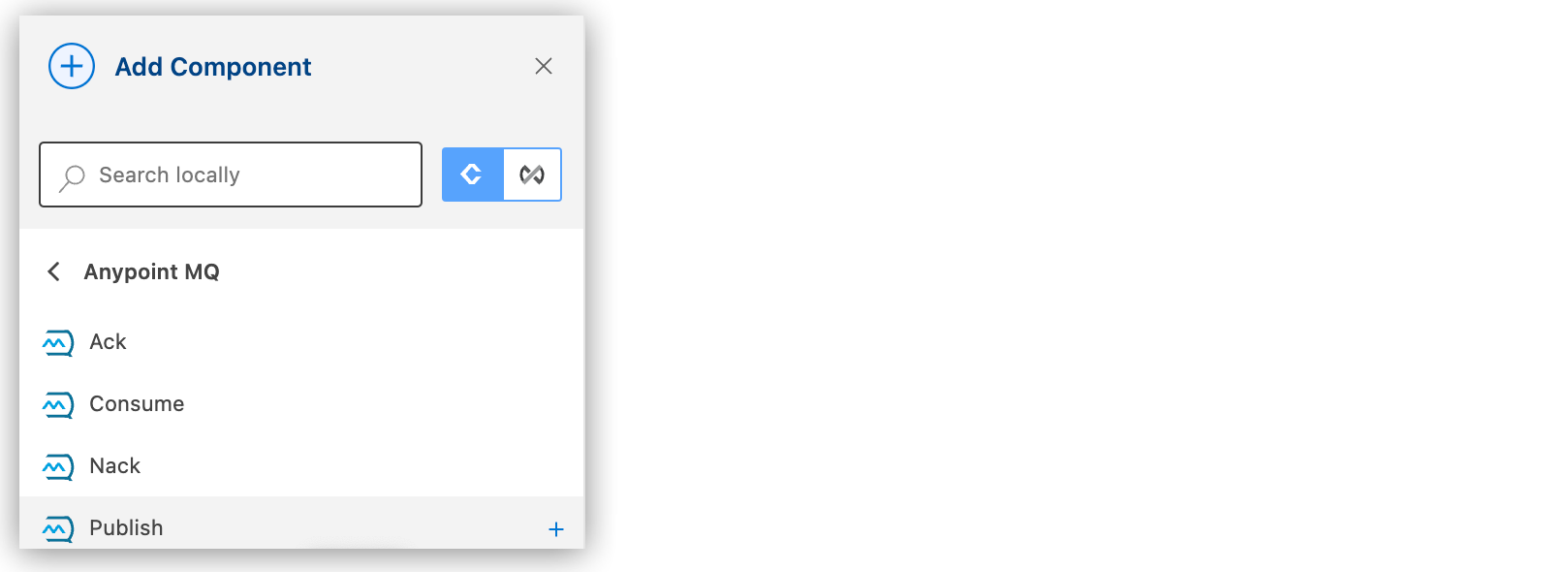
In the Add Component panel, click Connectors.
-
Click the connector name and then click the operation to add, such as Publish:
If the connector is not available locally, click the
 (Search in Exchange) toggle:
(Search in Exchange) toggle: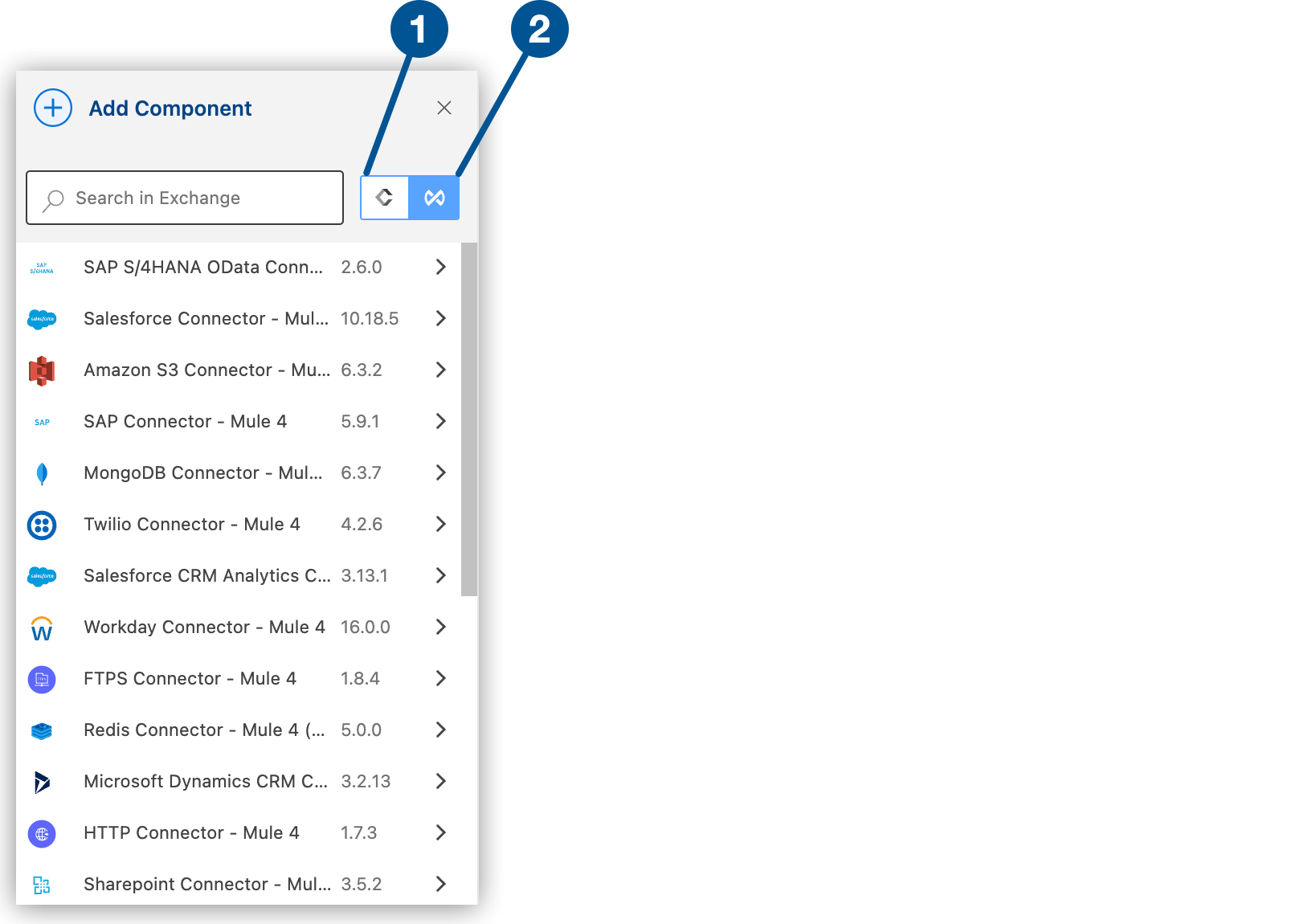
1 Search locally 2 Search in Exchange -
Select the connector to add to your project.
-
Select the operation from the Add Component panel.
-
Adding a connector to an integration project does not make that connector available to other projects in your Anypoint Code Builder workspace.
Configure a Source For the Flow
A trigger (source) starts the flow when specified conditions are met. If a connector has its own associated sources, you can use a connector-specific trigger to initiate the flow. Each connector trigger has a unique configuration.
You can configure the following sources for this connector:
-
HTTP > Listener
Initiates a flow each time it receives a request on the configured host and port
-
Scheduler
Initiates a flow when a time-based condition is met
For example, to configure an HTTP Listener trigger, follow these steps:
-
Click the Listener component on the canvas UI.
-
(Optional) Click the edit icon to change the name of the Listener component.
-
(Optional) If you created a configuration file for the connector, select it.
-
In the General tab, in the Path field, enter the relative path for the path set in the HTTP configuration element. See Configure Paths.
-
Select the Advanced tab to configure the following attributes:
Attribute Description Required Allowed methods
To allow all HTTP methods (default), do not define this attribute. To restrict certain methods, specify all allowed HTTP methods, for example,
GET, POST, as a comma-separated list.No
Response streaming mode
Whether to use streaming when the response is sent.
No
Output MIME type
MIME type of the payload that this component outputs.
No
Parameters
Appends a key-value pair for a reader property to the value of the Output MIME attribute. Multiple key-value pairs are allowed.
No
Output encoding
Encoding of the payload that this component outputs.
No
Streaming Strategy
Configures the way data streams are consumed in Mule apps.
No
Primary node only
Select this option to execute the Listener trigger on the primary node only when running in a cluster.
No
Redelivery policy
Configures the redelivery policy for executing requests that generate errors. You can add a redelivery policy to any source in a flow.
No
Reconnection strategy
When an operation in a Mule application fails to connect to an external server, the default behavior is for the operation to fail immediately and return a connectivity error. You can modify the default behavior by configuring the reconnection strategy for the operation.
No
Response
No
Error Response
HTTP error response returns a status code for the error.
No
Body
Body of the error message.
No
Headers
Headers to include in the error message.
No
Status code
Status code of the error response, for example,
500.No
Reason phrase
Reason for the error, for example,
Gateway TimeoutorInternal Server Error.No
For complete source configuration details, see the MCP Connector Reference.
Example: Configure a Tool Listener Source
A common use case is exposing operations as tools that MCP clients can invoke. In the XML editor, add a Tool Listener source to your flow:
<flow name="my-tool-flow">
<mcp:tool-listener
config-ref="MCP_Server_Config"
name="get-user-info">
<mcp:description><![CDATA[Retrieves user information by ID]]></mcp:description>
<mcp:parameters-schema><![CDATA[{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"userId": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["userId"]
}]]></mcp:parameters-schema>
</mcp:tool-listener>
</flow>Configure an MCP Connection
MCP Connector supports both client and server configurations with different connection types.
Configure an MCP Client Connection
Use client configurations to connect your Mule application to external MCP servers.
Streamable HTTP Client
The Streamable HTTP client connection enables load-balanced, scalable connections to MCP servers:
<mcp:client-config name="MCP_Client_Config" clientName="MCP Client" clientVersion="1.0.0">
<mcp:streamable-http-client-connection
serverUrl="https://mcp-server.example.com"
mcpEndpointPath="/mcp"
requestTimeout="30"
requestTimeoutUnit="SECONDS">
<mcp:default-request-headers>
<mcp:default-request-header key="Authorization" value="Bearer ${api.token}"/>
</mcp:default-request-headers>
</mcp:streamable-http-client-connection>
</mcp:client-config>SSE Client Connection (Deprecated)
The SSE (Server-Sent Events) client enables persistent, server-push connections:
<mcp:client-config name="MCP_SSE_Client_Config">
<mcp:sse-client-connection
serverUrl="https://mcp-server.example.com"
sseEndpointPath="/sse"
requestTimeout="30"
reconnectionDelay="500"
reconnectionDelayUnit="MILLISECONDS">
</mcp:sse-client-connection>
</mcp:client-config>Configure an MCP Server Connection
Use server configurations to expose your Mule application as an MCP server.
Streamable HTTP Server
<http:listener-config name="HTTP_Listener_Config">
<http:listener-connection host="0.0.0.0" port="8081"/>
</http:listener-config>
<mcp:server-config name="MCP_Server_Config"
serverName="My MCP Server"
serverVersion="1.0.0">
<mcp:streamable-http-server-connection
listenerConfig="HTTP_Listener_Config"
mcpEndpointPath="/mcp"
requestTimeout="10"
requestTimeoutUnit="SECONDS">
</mcp:streamable-http-server-connection>
</mcp:server-config>SSE Server Connection (Deprecated)
<http:listener-config name="HTTP_Listener_Config">
<http:listener-connection host="0.0.0.0" port="8081"/>
</http:listener-config>
<mcp:server-config name="MCP_Server_Config"
serverName="My MCP Server"
serverVersion="1.0.0">
<mcp:sse-server-connection
listenerConfig="HTTP_Listener_Config"
sseEndpointPath="/sse"
messagesPath="/message"
requestTimeout="10"
requestTimeoutUnit="SECONDS">
</mcp:sse-server-connection>
</mcp:server-config>Configure Authentication
MCP Connector client connections support standard HTTP authentication methods including Basic, Digest, NTLM, and OAuth. For detailed authentication and security configuration, see Applying Security to the MCP Server.
Add Operations to Your Project
Add components to your integration project to build a flow:
-
In the Explorer view, open the XML file for your project, such as
my-project-name.xml. -
Select Build a Flow from the start card to create an empty flow:
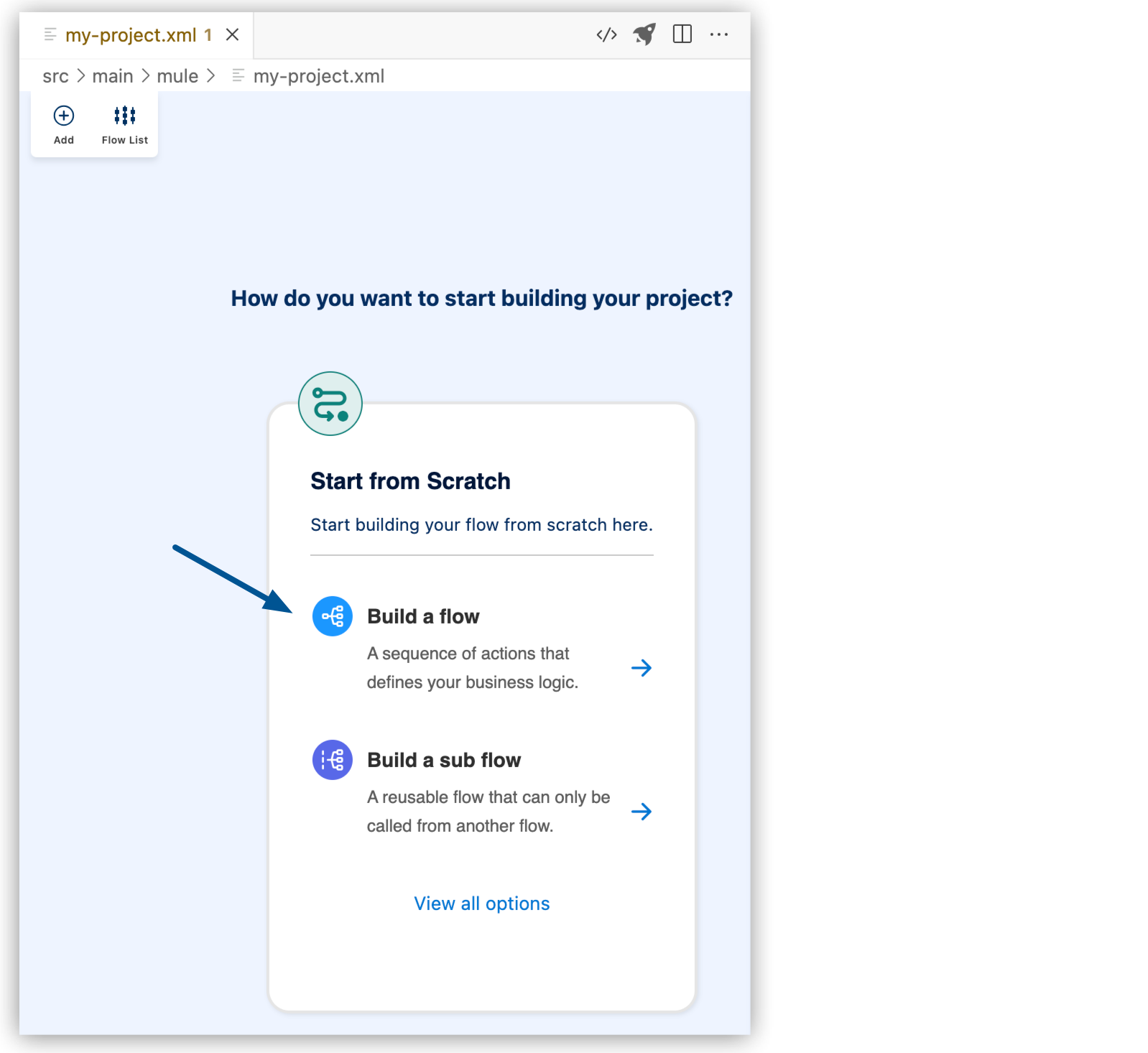
-
Change the name of the flow:
-
Click Flow.
-
Click the edit icon.
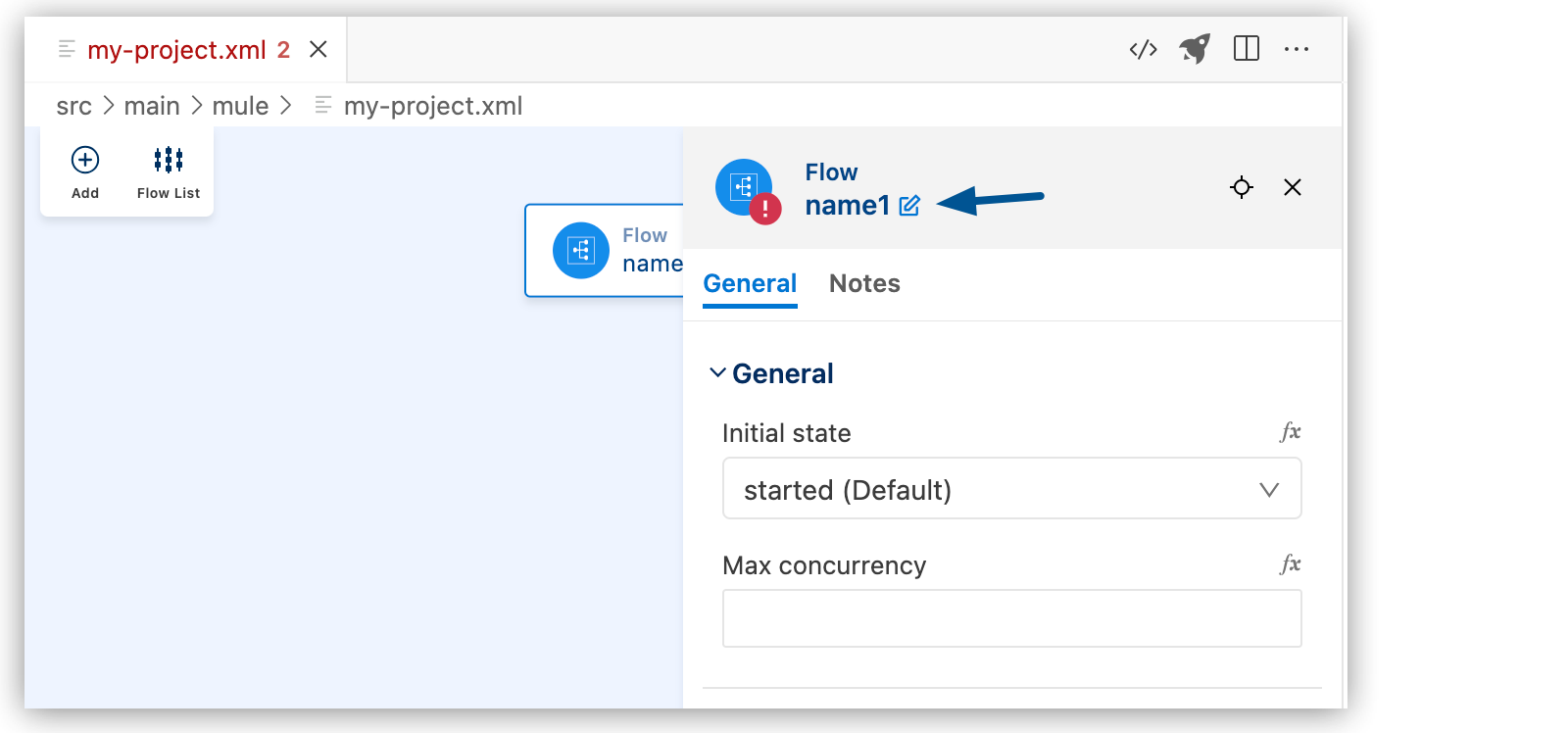
-
Enter the flow name, and click the checkmark.
-
In the canvas UI, click the
 (Add component) icon.
(Add component) icon. -
In the Add Component panel, search for and select your component from the results. The following example shows the Listener component from the HTTP search results:
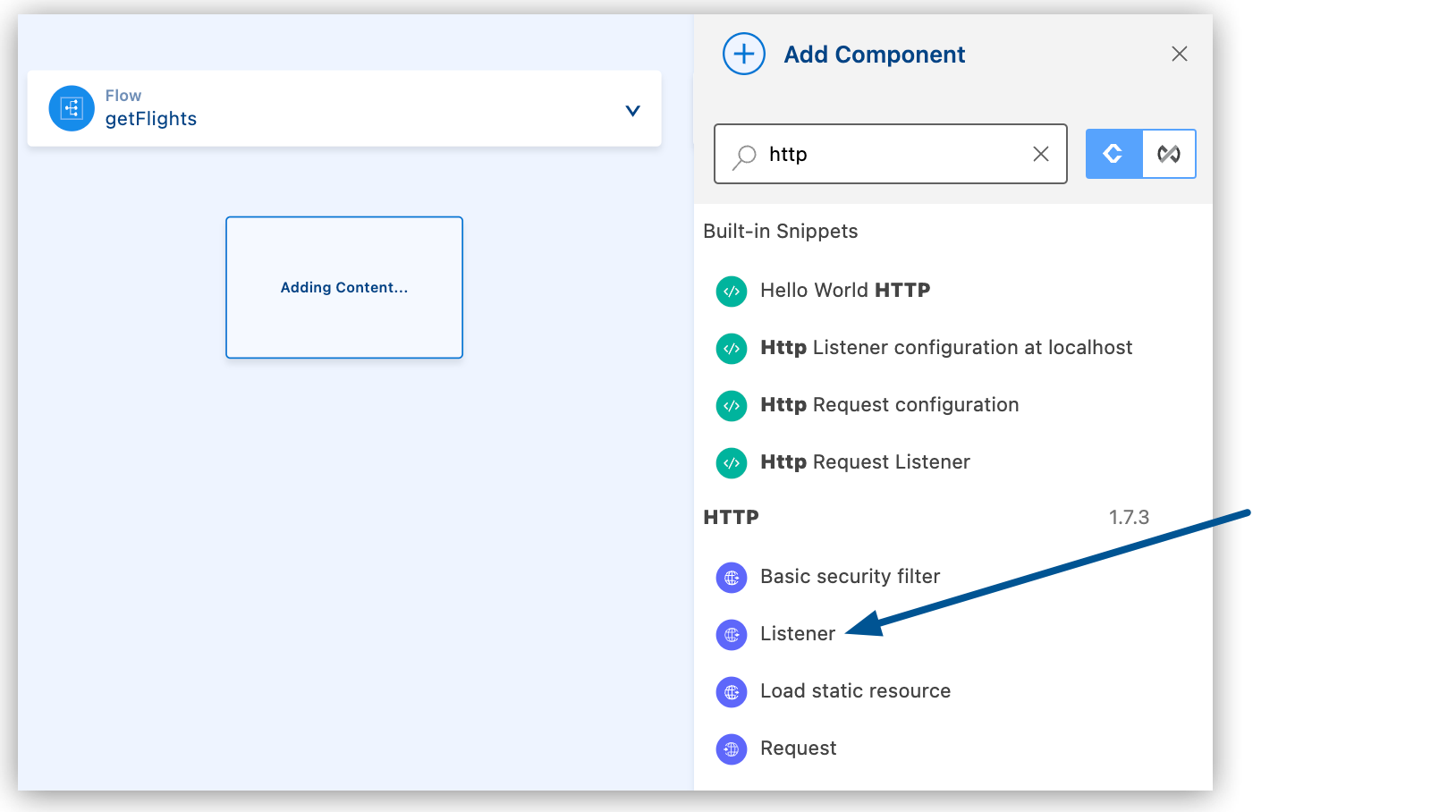
The configuration XML file now includes the XML for the HTTP Listener into the
<flow/>element, for example:<flow name="getFlights" > <http:listener path="" config-ref="" doc:name="Listener" doc:id="ojzfry" /> </flow>
-
For a complete list of operations and their configurations, see Supported Operations.
Example: Using Operations
After you configure a connection, you can add operations to interact with MCP servers (when configured as a client) or handle requests (when configured as a server).
Example of calling a tool on an MCP server:
<mcp:call-tool config-ref="MCP_Client_Config" name="get-user-info">
<mcp:arguments><![CDATA[#[{
"userId": payload.userId
}]]]></mcp:arguments>
</mcp:call-tool>Example of reading a resource from an MCP server:
<mcp:read-resource config-ref="MCP_Client_Config" uri="file:///documents/report.txt"/>For detailed information on each operation’s parameters and usage, see the MCP Connector Reference.
Configure TLS for Secure Connections
To secure connections with TLS:
<tls:context name="TLS_Context">
<tls:trust-store
path="truststore.jks"
password="${tls.truststore.password}"/>
<tls:key-store
path="keystore.jks"
password="${tls.keystore.password}"
keyPassword="${tls.key.password}"/>
</tls:context>
<mcp:client-config name="MCP_Client_Config">
<mcp:streamable-http-client-connection
serverUrl="https://secure-mcp-server.example.com"
tlsContext="TLS_Context">
</mcp:streamable-http-client-connection>
</mcp:client-config>Create a New Configuration XML File
Anypoint Code Builder creates the initial Mule configuration XML file in src/main/mule
within the Mule project.
This file contains global configurations and flow structures.
You can create additional configuration files, for example, to store global configurations.
To create a new XML configuration file:
-
In the Explorer view, right-click the mule folder (
src/main/mule) and select New File.Alternatively, use the menu.
Show me how
Select the
mulefolder, and then:-
In the desktop IDE, select File > New Mule Configuration File.
-
In the cloud IDE, click the
 (menu) icon, and select File > New File.
(menu) icon, and select File > New File.
-
-
Enter a name for the new file with the
.xmlextension. -
In the Editor view for the new file, press Ctrl+Space to display available options.
-
Select Empty mule configuration:
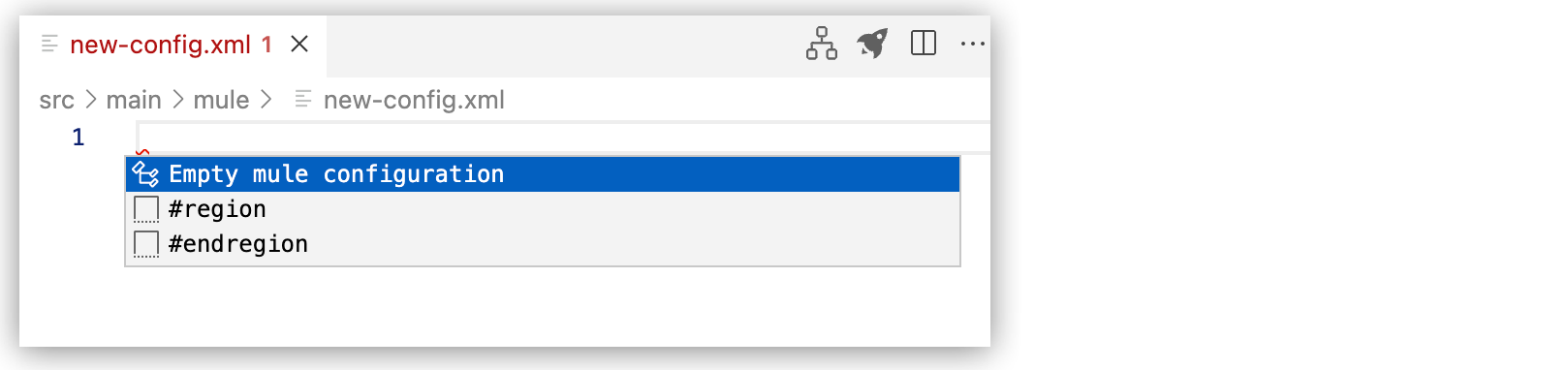
This command adds the following code to the file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <mule xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core" xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation" xmlns:ee="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/core" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/core/current/mule-ee.xsd"> </mule>
Deploy the App
These are available for deployment:
-
CloudHub 2.0
-
Runtime Fabric
-
Hybrid
-
CloudHub (with limitations, such as you can’t apply policies)
For more information about deploying apps, see Deployment Options.



