Managed Flex Gateway High Availability and Disaster Recovery Deployments
CloudHub 2.0 and Runtime Fabric manage Managed Flex Gateway replica deployments and control the gateway’s high availability and disaster recovery. To learn about how these deployment targets handle disaster recovery and high availability not specific to Flex Gateway, familiarize yourself with CloudHub 2.0 High Availability and Disaster Recovery.
This diagram shows how multiple Managed Flex Gateway replicas are deployed.
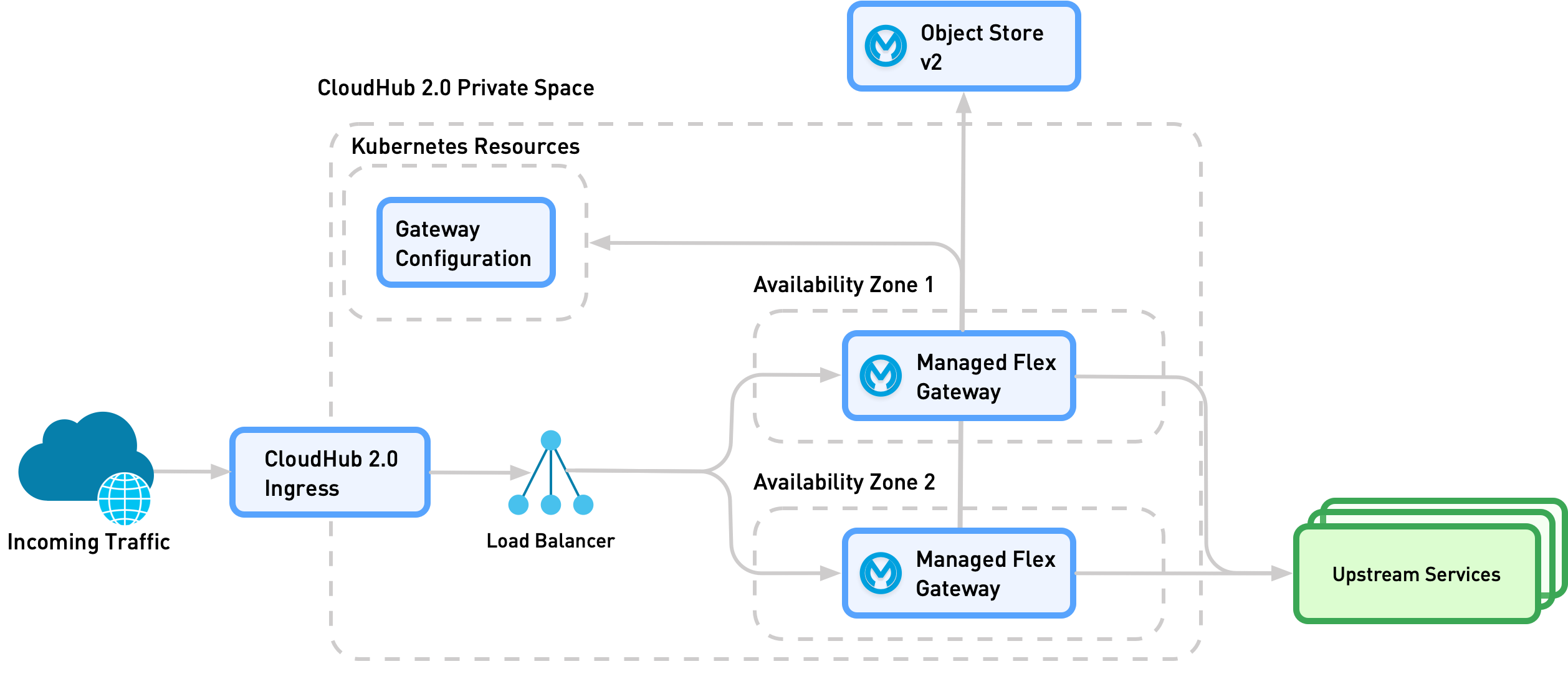
External traffic entering through private space ingress is distributed across a kubernetes service of Managed Flex Gateway instances. Replicas share the gateway configuration and data that must persist in a Kubernetes resource. Replicas share HTTP caching and distributed rate limiting data directly with each other.
| The diagram shows CloudHub 2.0 ingress. For Runtime Fabric, you must configure your own ingress. Your ingress must terminate TLS before forwarding the request to the Managed Flex Gateway. |
Managed Flex Gateway High Availability
The private space manages Managed Flex Gateway high availability by ensuring:
-
At least two Flex replicas are always available and distributed across different availability zones in the private space. Traffic is distributed to replicas and zones evenly using a round robin traffic distribution.
-
If a replica fails, a new replica is spawned. While respawning the replica, the outstanding replicas receive a temporary spike in traffic until the new replica can accept traffic. These short spikes in traffic are visible in monitoring as a temporary spike in CPU usage.
-
Overloaded gateways don’t abruptly stop incoming traffic processing as a result of overload. However, overloaded gateways show gradual degradation of response time for requests until CPU subsides.
-
-
Large and extra large Managed Flex Gateways have more capacity allocated per replica and autoscale up to three replicas across three availability zones depending on CPU usage.
Managed Flex Gateway Configuration Storage
Managed Flex gateway stores API configurations locally in the private space kubernetes service. Locally stored configurations enable the gateway to start faster than an equivalently configured Self Managed Flex Gateway (that needs to download the configuration from Anypoint upon start). Locally stored configurations provide a layer of resiliency in the unlikely event that the Anypoint control plane isn’t reachable during Managed Gateway startup.
Managed Flex Gateway does not store contracts locally. Upon starting, Managed Flex Gateway downloads contracts from Anypoint Platform. If an API uses contracts, for example if the client ID enforcement policy is applied, the gateway downloads the contracts before accepting traffic.



